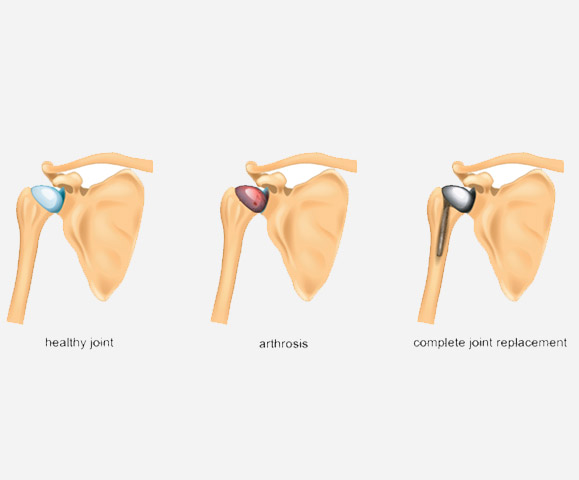
Shoulder replacement, also known as shoulder arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves replacing the damaged parts of the shoulder joint with an artificial joint. The surgery is typically recommended for people who have severe shoulder pain and stiffness, often caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or rotator cuff injuries.
During the surgery, the surgeon makes an incision to expose the shoulder joint and removes the damaged parts, including the ball-shaped head of the upper arm bone and the socket of the shoulder blade. The new artificial joint, which may be cemented or press-fit into the bone, is then implanted. The artificial joint is made of metal and plastic or ceramic materials, and is designed to mimic the natural shoulder joint.
After surgery, patients will typically need to stay in the hospital for a few days and participate in physical therapy and rehabilitation to help restore strength and mobility in the affected shoulder. It may take several weeks to months for patients to fully recover and return to their normal activities.
Shoulder replacement surgery has a high success rate and can provide significant relief from shoulder pain and improve mobility and quality of life. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications, including infection, blood clots, dislocation of the artificial joint, and implant failure.
It is important to discuss the benefits, risks, and potential complications of shoulder replacement surgery with your doctor to determine if it is the right option for you.